UNIT 4
I. Look up in the dictionary how to pronounce the following words. Write them down in the dictionary.
|
circular to assume decimal to handle |
octal a value cell a location uniquely |
contiguous selecting adequate precise |
comparing
sorting matching |
II. Read the text and do the exercises that follow it:
Information, machine words, instructions, addresses and reasonable operations
Information is a set of marks or sings that have meaning. These consist of letters or numbers, digits or characters, typewriter signs, other kinds of sing and so on. So, information is the end product of people obtained from computer systems. The process of using computer is circular beginning and ending with people.
When we see number 562 we normally assume that it represents five hundred and sixty-two. This is because we are conditioned to the decimal system where the base is 10. Nowadays school children are taught to handle numbers with different bases such as octal (8) and binary (2). With the number 562 we understand this to mean that we have 5 hundreds, 6 tens and 2 units (5 · 100 + 6 · 10 + 2 · 1) so each digit has a meaning represented by its value and its position.
Computers work by using the binary system where the base is 2. This means that each position can have a value of 0 or 1. So any information may be represented by the binary system including these two digits. Because at their most basic level, computers only understand the language of electricity: positive (or on or 1) and negative (or off or 0). Instead of going up in powers of ten (10,10 x 10,10 x 10 x 10) the positions go up in powers of 2 (2,2 x 2,2 x 2 x 2,2 x 2 x 2, etc.)
Thus the binary number 1001 can be represented as:
|
2 x 2 x 2s position |
2 x 2s position |
2s position |
units position |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Thus number can be converted to decimal
2 x 2 x 2 x 1 = 8 x 1 = 8
2 x 2 x 0 = 4 x 0 = 0
2 x 0 = 0
1 = 1
So 1001 in binary has the same value as 9 in decimal.
The memory of a computer consists of a large number of locations, each of which in uniquely addressable. In most modern computers these locations are called bytes. They consists of eight positions and each position can be set to 0 or 1. These positions are bits. A bit is the smallest part of information and it is the basic unit of data recognized by the computer. Bits are grouped in units that are called bytes. A byte consists of eight bits.
A group of contiguous bytes that can be manipulated together is called a word. A word may be 2 bytes (16 bits) or 4 bytes (32 bits) or other combinations. 16 bits can hold number up to 65,535. Word length is the term used to describe a word’s size in numbers of bits.
The memory of the computer can hold instructions that the control unit acts upon, and it can store binary numbers on which arithmetical operations can be carried out. A large number of business operations, and computer-based training in particular, do very little with numbers. They are mostly concerned with accepting as input, manipulating and presenting as output, large quantities of character information-names and addresses.
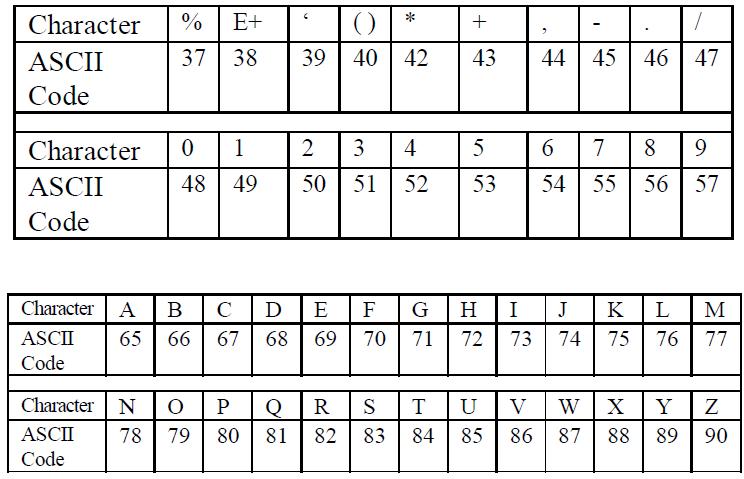
An address is the name of particular memory location or cell. Each memory location (word or byte) has it own unique address or number just a post office box. If one character is stored in a byte, there are 256 possible characters that the different bit patterns can represent. That is quite adequate for all alphabetic characters in upper and lower case, the number 0 to 9 and the various punctuation and special characters that are found on a typewriter keyboard. One widely used Coding convention is ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange), pronounced as the two words «ass» and «key».
This is a part of the ASCII Code
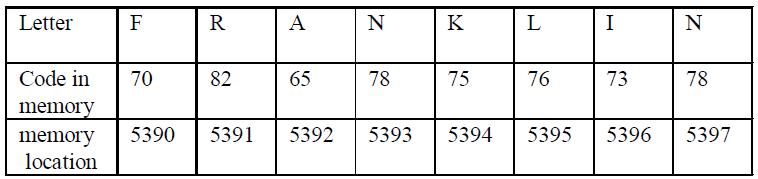
Thus, if we wanted to hold FRANKLIN in part of the correct answer it could be held somewhere in memory (say location 5390 onwards) as the following ASCII codes:
Computer people generally refer to 1000 (1024 to be precise) byte as a kilobyte (kb) and a million bytes as a megabyte (mb). So, if somebody has a microcomputer with 640 k memory locations than means there are 640,000 locations in the machine.
Reasonable operations are mathematical and logical. Mathematical operations include arithmetical and algebraic operations. Arithmetical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, taking a square root, etc.; and algebraic operations are called raising to a power as well as differentiating and integrating.
Logical operations include comparing, selecting, sorting, matching, etc.
III. Translate these into your own language:
1. a set of marks and signs
2. circular beginning and ending with people
3. we are conditioned to the decimal system
4. base
5. including these two digits
6. the positions go up in powers of 2
7. bytes
8. bits are grouped
9. can be manipulated together
10. to hold instructions
11. memory location
12. to include
IV. Translate these into English:
|
1. множество знаков 2. число представляет 3. учат работать с числами 4. у каждого есть свое значение 5. двоичная система исчисления 6. основной уровень |
7. десятичное число 8. запоминать, хранить в памяти 9. выполнять 10. точно 11. разумные операции
|
V. Fill in the necessary words:
1. ..... is a set of marks or signs.
2. We are conditioned to the ..... ..... .
3. Computers work by using the ..... ..... where the ..... is 2.
4. The ..... of a computer consists of a large number of locations.
5. A ..... is the smallest part of information.
6. A byte consists of 8 ..... .
7. The memory of the computer can ..... instructions.
8. Computer people generally ..... ..... 1 000 bytes as a kilobyte.
VI. Fill in the prepositions:
1. Nowadays school children are taught to handle numbers ..... different bases.
2. ..... their most basic level, computers only understand the language of electricity.
3. Instead of going ..... in powers of ten, the positions go ..... ..... powers of 2.
4. Each position can be set ..... 0 or 1.
5. Bits are grouped ..... units.
6. The memory can store binary numbers ..... which arithmetical operations can be carried ......
VII. Give the correct definitions of the following terms:
|
a) information |
c) bit |
e) word |
g) reasonable operation |
|
b) binary system |
d) byte |
f) address |
VIII. Answer the following questions:
1. What is information?
2. Do computers work by using binary or decimal system?
3. What is the base of the binary system?
4. How can any information be represented?
5. What is the ASC II Code?
IX. Write you last name in letters and codes in memory and in memory locations, use the ASC II Code.
X. Retell the text.
